25
2012
What is a Relational Database Management System or RDBMS?
Every webmaster knows how invaluable database system is in running and managing information in a website. Be it a small webstore with limited traffic or a gargantuan website with multiple server location, database system is an integral part of planning and development cycle of a company.
Relational Database Management System or RDBMS is one of the most famous and most widely used database management systems in the industry today. If you know Oracle or IBM’s DB2 database management system, you are most probably aware of the presence of Relational Database Management System. After all, these are only two of many RDBMS available worldwide. To further improve your understanding, here are some things you should know about RDBMS.
Relational Database Management System Explained
Edgar F. Codd first introduced relational DBMS in 1970 in his paper entitled “A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks” as well as in other papers where he operationally defined what he meant with “relational”. One of these papers is what is known as Codd’s 12 Rules, which define what makes up RDBMS.
In its elementary form, relational database is a shared data repository, which can be used to present relationships among information and to retrieve, update and store data efficiently. The Relational Database Management System or RDBMS is using this idea of a relational database, along with a set of programs, to do its functions. These functions, at the very least, include presenting the data as relations and providing relational operation that could allow user to manipulate the data stored.
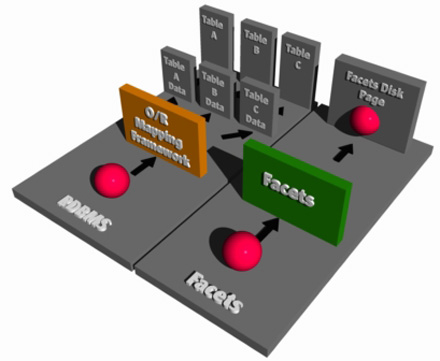
Almost all RDBMS available today runs on Standard Query Language. Albeit there are attempts to use other programming languages like C++, none has been commercially feasible. Apart from SQL, one of the defining features of RDBMS is the use of tables and presentation of data and relationships in tabular form. Tables are used in RDBMS to define and describe a particular data.
Choosing the Best RDBMS for You or Your Company
Not all RDBMS is the best for you, your website and your business. Sometimes, a cheap and simple system is not enough to do the task, and sometimes, the high-end RDBMS is not the right and efficient way to go. To choose your RDBMS, you can select the ones that fit your needs best with categories like:
1.) administrative requirements
2.) administrative tools
3.) feature performance
4.) price.
Basically, administrative requirements and tools define how much attention a particular system needs and how many tools are available for the user when tweaking the system. Feature performance, on the other hand, generally refers to the performance of several features that comes with the DBMS. Such facet includes simple application as well as other aspects like replication, referential integrity and more. The last consideration for choosing a particular RDBMS is the price. Price includes everything the user has to pay for, and this includes license, support, maintenance costs and more. DBMS giants like Oracle and DB2 charges for licenses, while others like MySQL give user licenses for free.
Further readings
Advertisements
Recent Posts
- What is a Disaster Recovery Data Center
- What is a Relational Database?
- What is a Flat File Database?
- What is a DSN or Database Source Name?
- What is a Disaster Recovery Plan?
- What is an Open Source Database?
- What is Disaster Recovery?
- What is a Database Cluster?
- What are Database Servers?
- What are Database Forms?
Random Posts
- What is a Database Query?
- Database Software Options
- What is an Open Source Database?
- What is a Transactional Database?
- What are High Availability Servers?
- What Are Disaster Recovery Services
- What is a PostgreSQL Database?
- What is a Database Table?
- What is a XML Database?
- Installing your first WordPress script

 An article by
An article by 




